Tohoku University
Center for Data-driven Science and
Artificial Intelligence
Professor
Minoru Kuribayashi Ph.D
TEL: +81-22-795-3376![]()
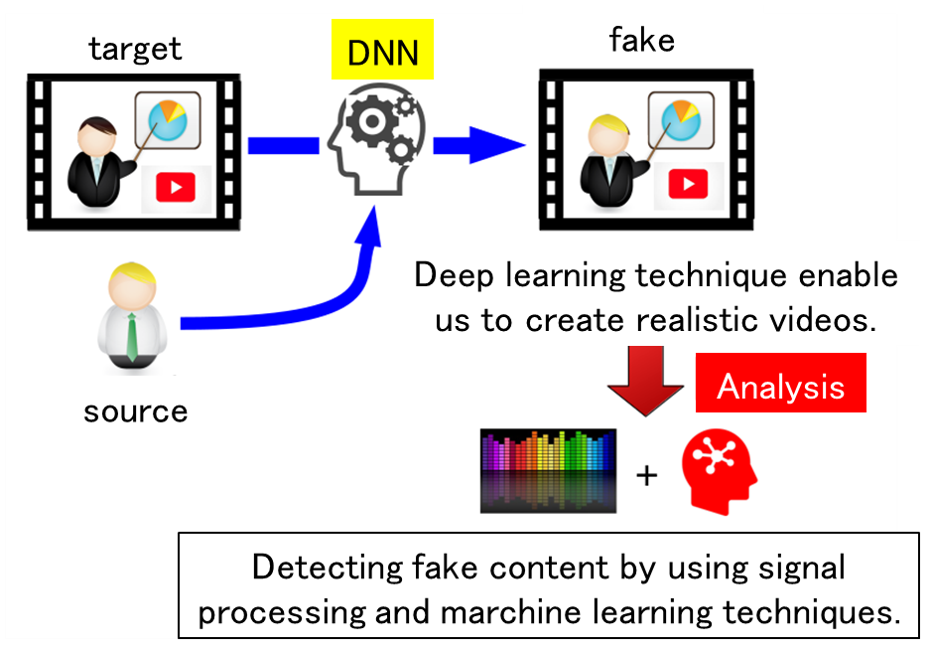
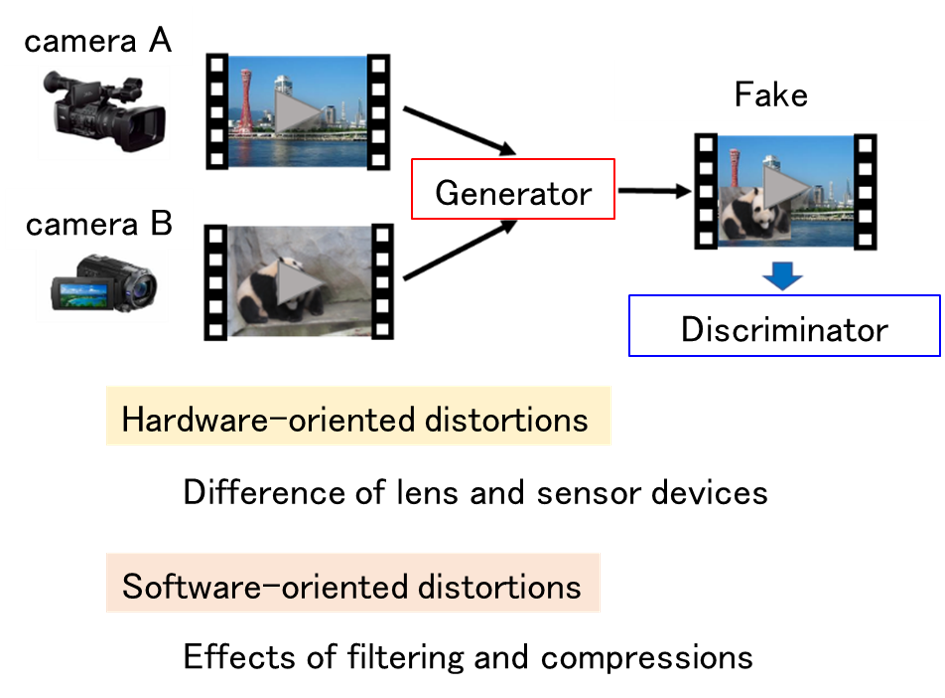
Classification of Fake Contents
By using deep learning technology with multiple videos of a person as supervised data, it is possible to create fake contents that realistically reproduce false statements. It has been pointed out that if this technology is misused to create fake content and spread it over the Internet, it could have a significant impact. In order to cope with this problem, it is necessary to develop a technology to determine “artificially created contents” and “normal content”. In this research, we aim to develop a system to classify whether or not the target content has been created by artificial processing.
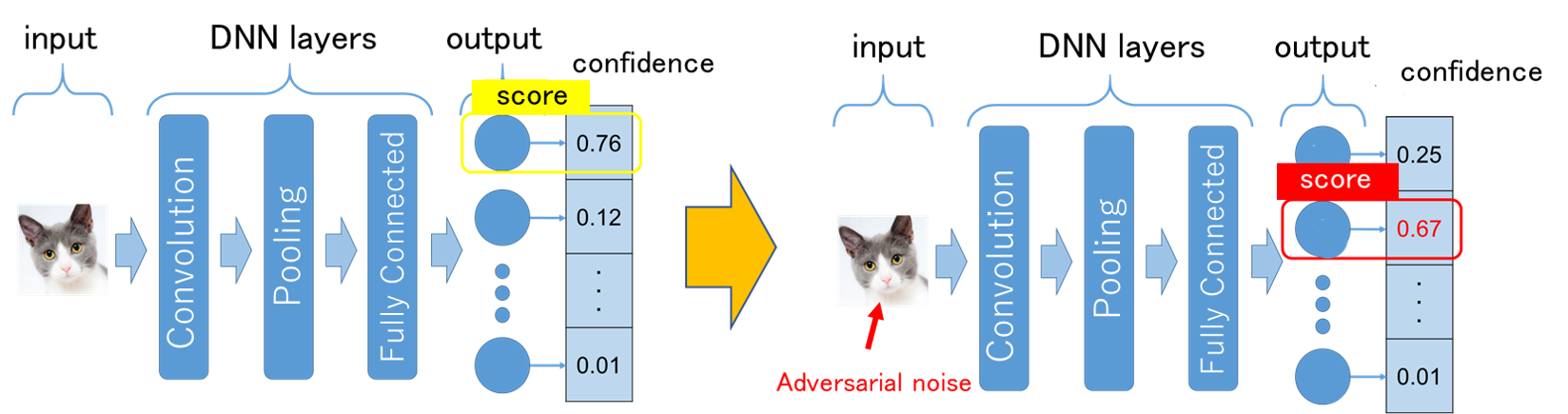
Detection of Adversarial Examples
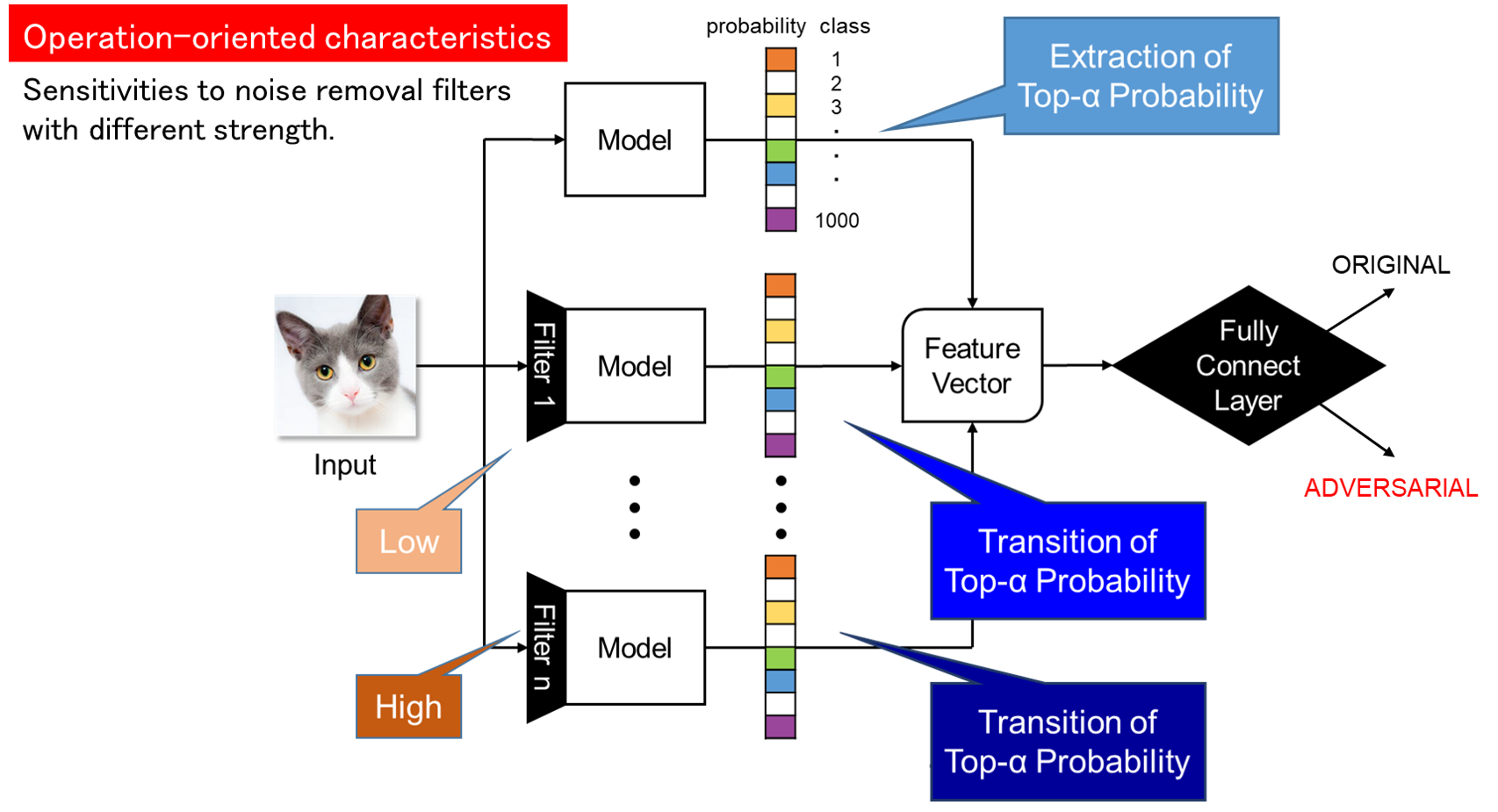
Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) have been applied to image recognition in many research fields such as face recognition and automatic driving. However, there is a problem that it is possible to make the CNN image recognition system detect false positives by intentionally adding noise. This problem is called adversarial examples, and it is an unavoidable characteristic of machine learning classifiers. In this research, we aim to protect the integrity of the machine learning system by preprocessing the image input to the image recognition system to classify whether it is a normal image or an adversarial case with intentional noise.
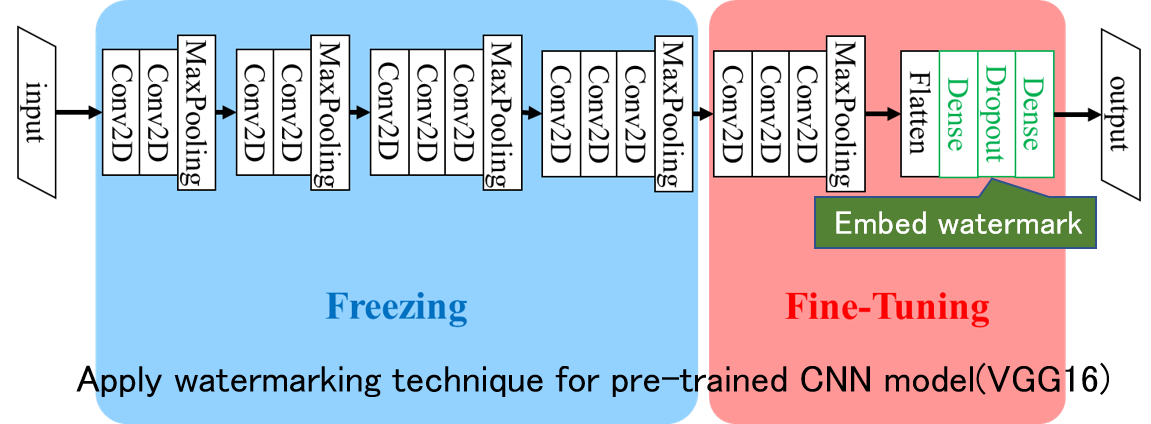
Watermarking for DNN Model
In order to efficiently develop systems based on deep learning using neural networks, it is important to share DNN models that have been trained using big data. To create such trained models, a lot of processing power and a huge amount of dataset are required. The weights of the trained models are of great value, and it is necessary to prevent the models from being easily copied and misused. In this research, we address this problem by embedding a watermark during training of DNN models. Unlike multimedia content such as images, video, and audio signals, we aim to realize a method that cannot be easily removed while minimizing the performance degradation of DNN models by embedding watermark information.
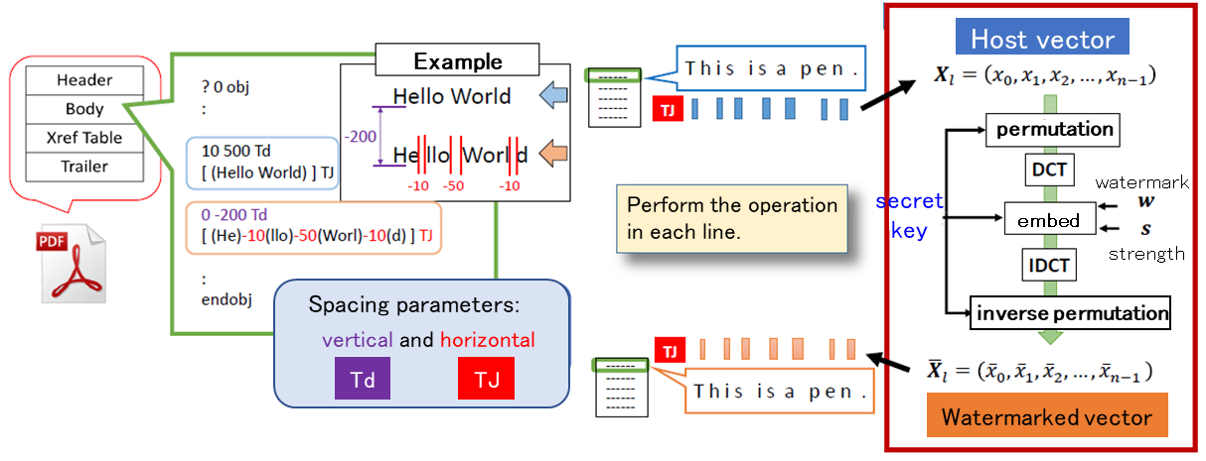
Data Hiding for PDF files
Watermarking technology has mainly dealt with digital content such as images, videos, audio, etc. On the other hand, in digital libraries and information distribution services for office documents, most of the leaked content are electronic documents. In this research, we focus on PDF files, which are widely used as a de facto standard, and apply watermarking technology to them by making good use of their file structure.
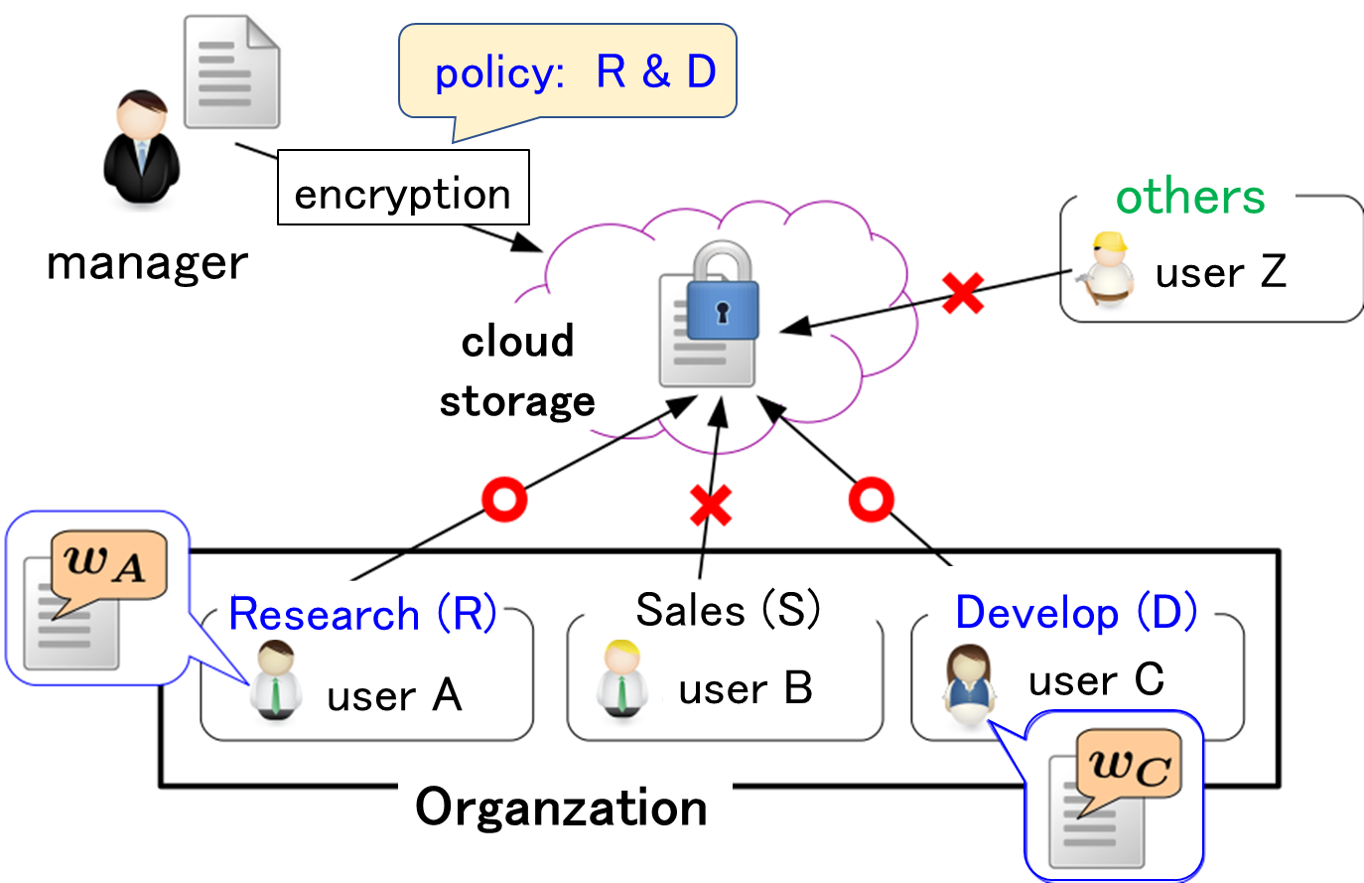
Secure Management System of Office Documents
With the digitization of document files, countermeasures against unauthorized processing have become an urgent issue. Countermeasures against information leaks and tampering have been important for a long time, and the application of cryptography has been used as the main means. However, in the case of leaks due to internal crimes, the use of advanced cryptographic processing is not effective against criminals who have decryption keys. In this research, we aim to realize a system that automatically stores browsing history in files for users with access privileges.
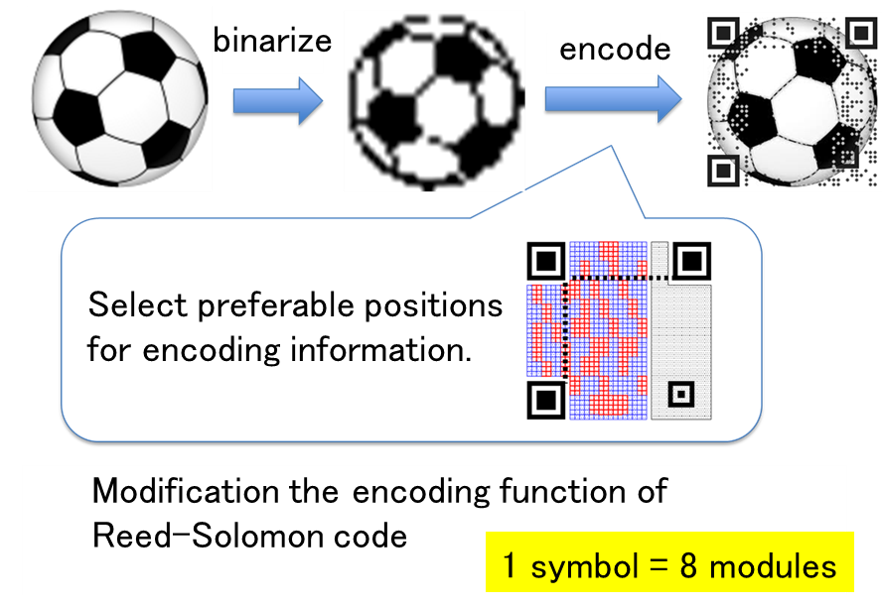
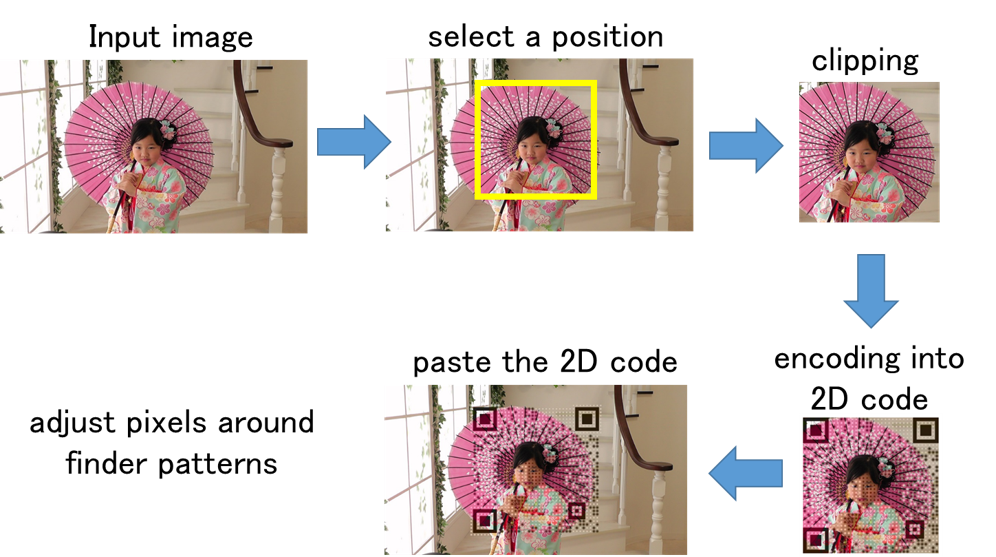
Designing 2D Codes and its Application
A standard 2D code consists of only black and white modules, and its appearance is a random pattern. On the other hand, it is possible to display images such as logos on 2D codes by changing the error correction function and the shape of the modules. In this study, we are developing an application to create 2D codes that can be read by normal applications while maintaining the quality of the displayed image by changing the coding function of the error correction code. In order to insert a 2D code into an image without much degradation in image quality, we devised a coding method that avoids visually important parts of the code and does not change the structure of the normal code.
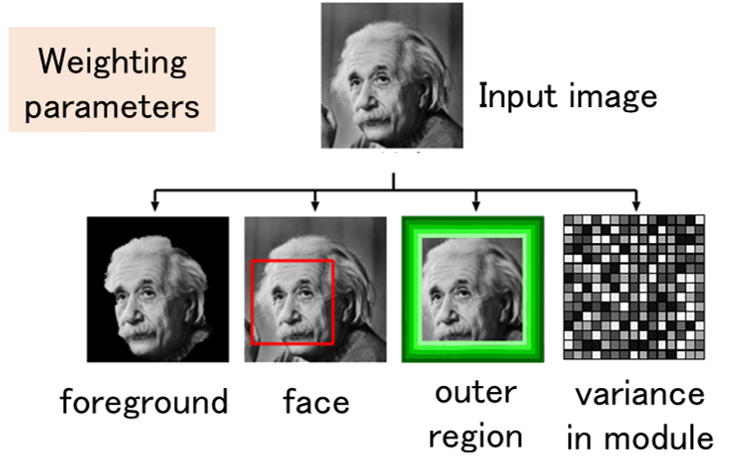
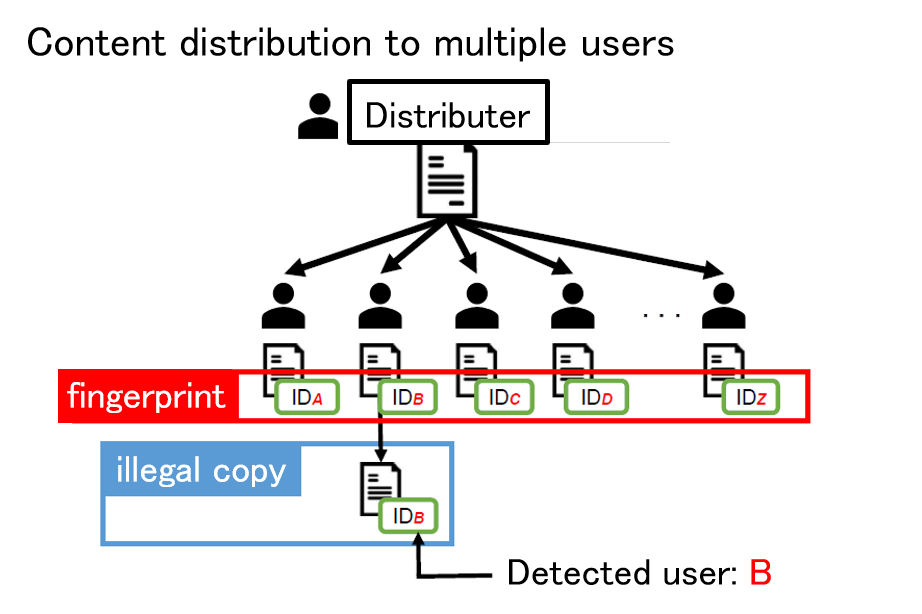
Digital Fingerprinting
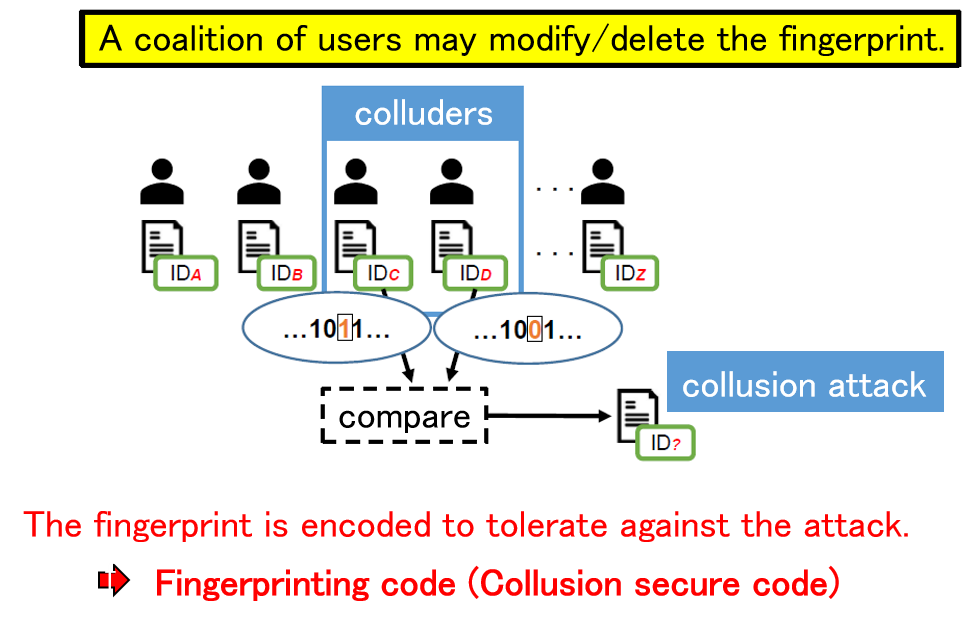
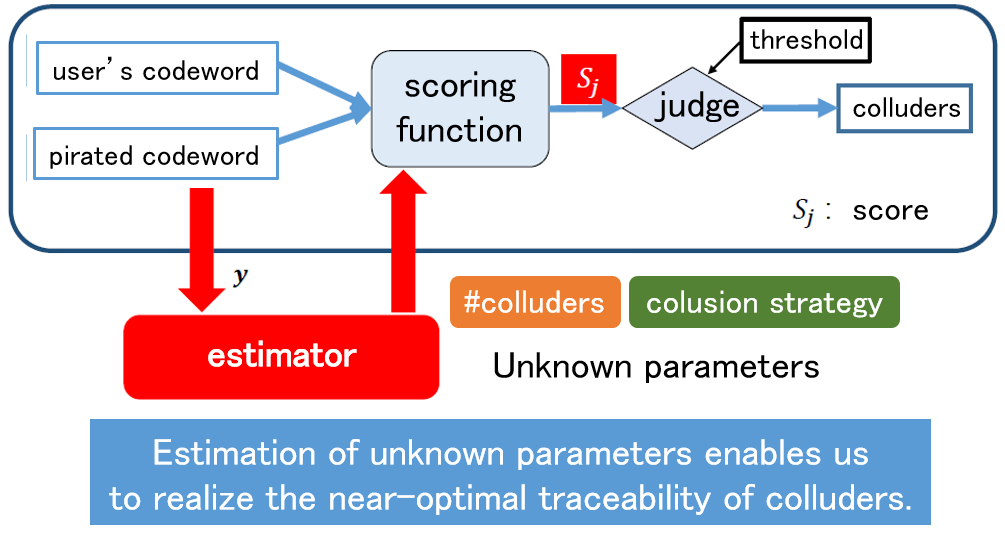
As a countermeasure against unauthorized copying, digital fingerprinting is a method of embedding different identification information in each piece of content using digital watermarking technology when the content is distributed to multiple users. If this identification information is correctly extracted when unauthorized copying is detected, the user who made the unauthorized copy can be uniquely identified. On the other hand, if a coalition of users compares their contents and analyzes the differences, it may not be possible to correctly identify the colluders. Such an attack is called a collusion attack, and collusion-resistant codes have been devised as a countermeasure. Since the publication of a code construction method with the theoretically shortest code length, attention has been focused on decoding methods to identify the collders, and theoretically optimal decoding methods have been devised. In this research, we use signal processing and machine learning techniques to achieve parameter estimation of collusion attacks from signals extracted from an illegal copy, and to obtain properties that are very close to the optimal decoding method.